WHAT
What Are Crypto Currencies?
Today we want to highlight a couple of information about crypto or also known as cryptocurrencies. blockchain technology is in everyone’s head so it is time for us to look into it.
Last Updated: 27.2.2025
Stable Coin vs Token vs Coin
Here’s a breakdown of the differences between stablecoins, tokens, and coins:
Stablecoin
A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency specifically designed to minimize price volatility, which is common in most cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Stablecoins achieve this by being pegged to a reserve of assets, most often a fiat currency like the U.S. Dollar, but sometimes they can be pegged to commodities like gold. The goal is to maintain a stable value, typically 1:1 with the underlying asset it’s pegged to.
The stability of stablecoins makes them particularly useful for trading, storing value, or transferring funds in the cryptocurrency space. For instance, if you want to avoid the price swings of Bitcoin, you could convert your Bitcoin into a stablecoin, keeping your funds within the crypto ecosystem but avoiding the volatility. They can also be used in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications or as a form of digital cash, making them a bridge between the traditional financial system and the crypto world.
How it works: Stablecoins typically maintain their peg through various mechanisms. The most common approach is for the issuer to hold reserves of the fiat currency (like USD) or other assets equal to the value of the stablecoins in circulation. There are also algorithmic stablecoins that use algorithms and smart contracts to regulate supply and demand to keep the price stable.
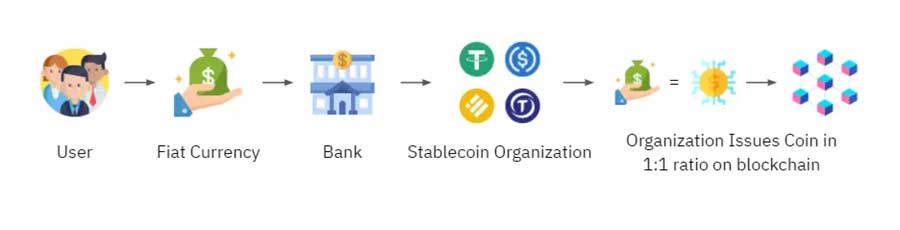
How centralized Stablecoin works
Examples:
- Tether (USDT)
- USD Coin (USDC)
- Dai (DAI)
Purpose: Stablecoins are often used by traders and investors to avoid the price volatility of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, while still being able to transact in the crypto ecosystem. They are used for trading, as a store of value, or in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
Token
A token is a type of cryptocurrency that operates on top of another blockchain. Unlike coins, which are used as digital currency within their own blockchain (like Bitcoin or Ethereum), tokens are typically created on existing platforms like Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain using smart contracts. Tokens can represent a wide range of things, such as ownership of a digital asset, voting rights in a decentralized organization, or even access to a service or platform.
Tokens come in different forms and serve various purposes. Some tokens represent ownership in a company or project, while others are used to power decentralized applications (dApps) or provide utility within a specific ecosystem. For example, in decentralized finance (DeFi), tokens can represent a claim on future profits or allow users to participate in governance decisions about the future of a protocol.
How it works: Tokens are created using smart contracts on a blockchain. On Ethereum, for instance, the ERC-20 and ERC-721 token standards are commonly used. ERC-20 tokens are interchangeable and can be used for a wide range of purposes, while ERC-721 tokens are non-fungible and typically represent unique items, like digital art or collectibles (NFTs).
Examples:
- Uniswap (UNI): A governance token for the Uniswap decentralized exchange.
- Chainlink (LINK): A token used within the Chainlink network for data services.
- Ethereum-based tokens (ERC-20, ERC-721): These tokens represent assets or are used within Ethereum-based smart contracts and dApps.
Purpose: Tokens can represent assets (like equity, commodities, or other currencies), utilities (access to a platform’s features), or even voting rights (in governance). They typically rely on other blockchains, such as Ethereum, to exist.
Coin
A coin refers to a cryptocurrency that operates on its own native blockchain. This blockchain is built to support its specific digital currency, and the coin is used primarily as a medium of exchange, a store of value, or a method of securing the network through a consensus mechanism (like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake).
For example, Bitcoin operates on the Bitcoin blockchain, and its primary purpose is to serve as a decentralized digital currency. Ethereum’s native coin, Ether (ETH), is used to pay for transactions and computational services on the Ethereum network. Coins, unlike tokens, are not built on top of other platforms. They are native to their blockchain and serve as the main method of exchange within that ecosystem.
How it works: Coins are usually mined or earned through a consensus mechanism (such as mining in proof-of-work or staking in proof-of-stake systems). The blockchain behind the coin validates and records transactions and these coins are used to pay for network fees or as a store of value.
Examples:
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, operating on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Ethereum (ETH): The native currency of the Ethereum blockchain, used for paying for transactions and running smart contracts.
- Litecoin (LTC): A coin that operates on its own blockchain similar to Bitcoin.
Purpose: Coins typically function as digital money and are used for making payments, transferring value, and securing blockchain networks. They are not dependent on any other blockchain for their operation.
Key Differences:
- Stablecoin: A stablecoin’s main feature is its stability in price. It’s often pegged to a fiat currency like the U.S. Dollar to reduce the typical volatility seen in cryptocurrencies. Stablecoins are used for transactions, as a store of value, or in DeFi, and they can be a safer, more predictable way to interact with crypto.
- Token: A token is a cryptocurrency that is built on top of an existing blockchain like Ethereum. Tokens can serve many purposes: they can be used for access to services, governance, or representing assets. Unlike coins, which have their own blockchain, tokens rely on the security and functionality of the blockchain they are built on.
- Coin: A coin is a cryptocurrency that has its own blockchain and is typically used as digital money. It is primarily used as a medium of exchange or for transactions. Coins like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin operate independently of other networks and serve as the backbone of their respective blockchains.
Tether (USDT) is a type of cryptocurrency known as a stablecoin. It is designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to a fiat currency, typically the U.S. Dollar. For every USDT in circulation, Tether claims to hold an equivalent amount of U.S. Dollars (or assets that can be easily converted to U.S. Dollars) in reserve.
The primary purpose of Tether is to provide cryptocurrency users with a stable alternative to other more volatile digital currencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. This makes USDT a popular choice for traders who wish to avoid the fluctuations of the broader cryptocurrency market, while still taking advantage of the speed and ease of cryptocurrency transactions.
The supply of USDT can expand or contract based on demand and the amount of fiat reserves the company holds. Since it is pegged to the U.S. Dollar, Tether can mint or burn USDT to maintain this peg.
USDT can be used for trading, transferring value between exchanges, or storing wealth in a more stable form compared to other cryptocurrencies.

