WHAT
What IS A BLOCKCHAIN?
Whether you’ve studied cryptocurrencies in a personal or academic context, or perhaps stumbled upon them in an article, you’ve likely encountered discussions about blockchain technology.
Last Updated: 27.2.2025
Blockchain explained
While blockchain is most commonly linked to cryptocurrencies, its innovative applications are quickly spreading to other industries. These applications cover areas such as data tracking, national currencies, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), sparking curiosity about the full potential of blockchain. So, what can blockchain actually do?
It turns out, a lot. Blockchain technology is already part of our lives, often without us even realizing it. But what makes blockchain so noteworthy? To explore this, Stanford faculty, and experts in the field, provide valuable insights, including through their course on Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technologies.
If you’re eager to understand the fundamentals of blockchain and how it works, keep reading for an introductory overview.
Understanding Blockchain
As the name suggests, a blockchain consists of blocks of data that are securely linked together in a digital chain. This data is stored in a decentralized, open-source system where each participating computer can verify the information. Rather than being managed in a centralized manner, blockchain operates without a hierarchical structure, ensuring greater trust, validity, and usability.
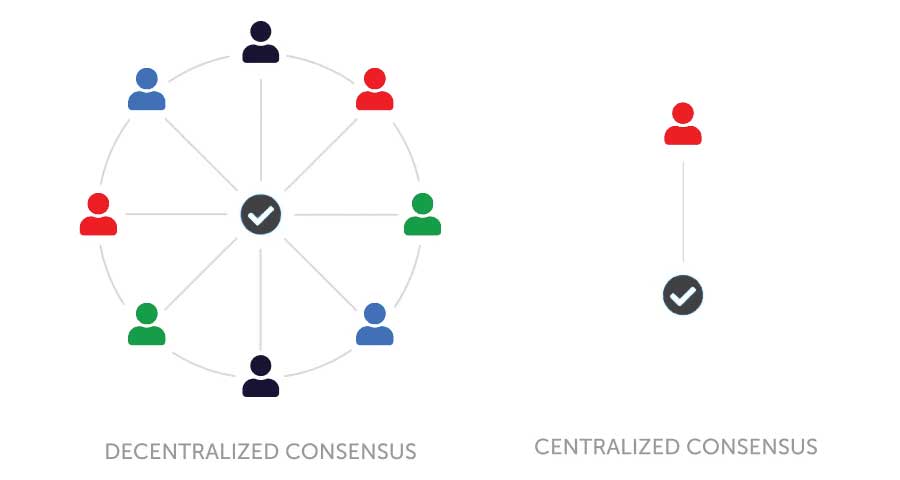
Decentralized vs Centralized consensus
Blockchain is an evolving field that plays an increasingly important role in online transactions and has applications in diverse areas. However, understanding how blockchain works can be tricky due to technical terms like “proof of work,” “proof of stake,” “miners,” and “distributed ledger technology.” Breaking these down and explaining the process behind a basic cryptocurrency transaction can make the technology more understandable.
Key Blockchain Terminology
Since blockchain can be overwhelming with all its technical jargon, let’s look at some key terms and the process of a cryptocurrency transaction.
- Blocks: These are the ledger entries that are constantly updated with data, forming an immutable record. Transactions are added to these blocks and synchronized across all participating nodes in the blockchain. The term “block height” refers to the total number of connected blocks at any given time, which grows as new blocks are added.
- Distributed Ledger: Blockchain operates on a distributed ledger, meaning that transaction records are shared across all parties involved, regardless of location. Ledgers can be permissioned (restricted access) or unpermissioned (open to the public).
- Security and Immutability: A key feature of blockchain is its resistance to tampering. Since each transaction is recorded across multiple copies of the ledger, modifying data in one place would be easily detected. This decentralized system makes it difficult for attackers to alter transaction histories or perform fraudulent activities like “double-spending.”
- Cryptographic Hash: Each transaction within a block is encrypted using a hash function, which turns input data into a unique alphanumeric string. This “digital fingerprint” is one-way, ensuring privacy and security while maintaining consistency across all copies of the blockchain.
- Digital Signatures: Blockchain uses public and private key pairs to authenticate transactions. The public key acts as an identifier, while the private key is used to sign and verify transactions. The combination of both keys ensures the legitimacy of the transaction and prevents tampering.
How does a transaction get into the Blockchain?
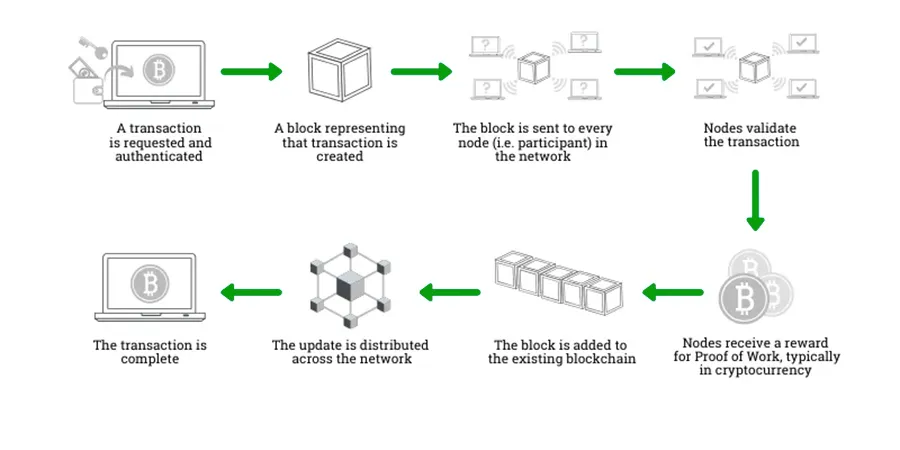
The validation process of a block with data in a blockchain
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
In blockchain, validating transactions and adding new blocks to the chain requires a consensus mechanism. Two of the most common mechanisms are Proof of Work and Proof of Stake:
- Proof of Work (PoW): This method, used by Bitcoin and Ethereum, involves miners solving complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. The first miner to solve the problem gets rewarded with newly minted coins. However, this process requires significant computational power and energy consumption.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In PoS systems, validators “stake” their cryptocurrency to participate in the block creation process. The more currency staked, the higher the chance of being chosen to verify a transaction. PoS systems are more energy-efficient than PoW, as they don’t require heavy computational work. Ethereum is transitioning from PoW to PoS in 2022 to reduce energy usage and increase fairness.
In both systems, the goal is to maintain the integrity of the blockchain, ensuring that all transactions are legitimate and verifiable.
Smart Contracts and Digital Assets
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain can be used for smart contracts—self-executing contracts where the terms are written into code. These contracts automatically execute once certain conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries like lawyers or notaries. Ethereum is a popular platform for smart contracts, enabling decentralized applications (dApps) that go beyond cryptocurrency trading.
The Origins of Blockchain
The concept of blockchain dates back to 2008 when an individual (or group) under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” The following year, Bitcoin was launched, using blockchain technology to create a decentralized currency system.
The key idea was to establish a public ledger for transactions, allowing each computer or node in the network to have a copy of the transaction history. The first-ever Bitcoin transaction occurred soon after the release of the cryptocurrency, proving that the system worked.
The Significance of Blockchain
Bitcoin’s blockchain allowed for the creation of digital money without the need for a centralized authority. Previous attempts at digital currency had been prone to fraud and counterfeit, but blockchain solved these problems by ensuring secure, verifiable transactions. Blockchain’s decentralized structure means that no single entity controls the system, and transactions are protected by cryptography.
This groundbreaking technology has since expanded beyond cryptocurrencies to a wide range of applications in industries such as healthcare, supply chain management, and even voting systems. Blockchain’s transparency and security make it an attractive solution for improving efficiency and trust in many sectors.
Blockchain’s Popularity and Potential
While cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum remain the most well-known use cases for blockchain, industries are increasingly recognizing their broader potential. Blockchain can be applied to track assets, protect user data, and streamline processes in numerous fields.
- Supply Chain Tracking: Companies like Dole Foods are using blockchain to track the journey of their products, providing customers with information about food quality and origin.
- Healthcare: Companies like Anthem are implementing blockchain to allow customers secure access to their healthcare data, promoting transparency and customer control.
- Global Impact: From the UN’s iris scanning ID system to supply chain management in the Netherlands, blockchain is making an impact worldwide, expanding far beyond financial applications.
Blockchain is expanding globally, from home equity loans in California to oil production in the Netherlands, and the UN’s iris scanning ID system. These applications highlight blockchain’s growing impact across various industries.
Conclusion
Blockchain is an incredibly versatile technology that is transforming industries from finance to healthcare. Its ability to provide secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions makes it a valuable tool in today’s digital world. While Bitcoin may have been the first major application of blockchain, its potential uses are rapidly expanding, and the technology is poised to revolutionize the way we manage data and conduct transactions in countless industries.

